A discoid meniscus is a meniscus shaped disk or dish instead of having the characteristic of a meniscus semilunar form "C"; i.e. There is no central opening that allows you to increase the depth and improve the coupling. Some patients have discoid meniscus and have no symptoms, there are children begin their symptoms at an early age. The cause is unknown.
ANATOMY:
Meniscus are cartilage structures that have the function of absorbing mechanical loads of the knee to avoid friction between both the upper femur and tibia below.
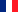
Fig. 1. normal meniscus of the knee with lateral discoid meniscus (note the thickness)
Normal meniscus have a "C" shape but the discoid has a half-moon shape which makes it more susceptible to tears. Some of the ligaments that hold the meniscus may be absent in the discode making it unstable i.e. which moves within the knee which explains the symptoms.
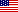
Fig. 2 types of blue (normal, incomplete, full) Discoid meniscus
SYMPTOMS:
The most common symptoms of the broken discoid meniscus are:-pain, swelling of the knee, feeling of brincoteo in the knee, blocking or pseudobloqueo, inability to extend the knee, lameness.
DIAGNOSIS:
Physical examination is very important, you have a series of signs and symptoms., imaging studies to confirm diagnosis such as: conventional radiography (mainly to see Oseas secondary lesions), and magnetic resonance imaging, this study detects soft tissues such as the meniscus and ligaments of knees and can tell us if the meniscus is discoid and if the ligaments that hold the meniscus are presentIf the meniscus is broken, dislocated, or if there are more injuries.
Fig. 3 magnetic resonance of a discoid meniscus (see thickness and the intensity of the signal)
TREATMENT:
The meniscectomy, Arthroscopic holmiun yag laser is the treatment of choice, without general anesthesia, without hospitalization and no scar it is perfectly possible to restore normal appearance that her meniscus must have, the laser making a cut only, and must to reducing intervention time and specifying the architecture that you want to give to the knee found. Occasionally, it is necessary to return part of the meniscus and combine in this way both procedures in the interest of advancing the total recovery of the patient. We can say that the person has 95% likely to be satisfied of the final result.