The surface of your knee is covered with an adhered, elastic tissue which fulfills an important role regarding joint harmony, this tissue is denominated cartilage, which lubricates, cushions blows, and gives stability to the knee. A small portion is may be injured in which case a condition known as chondropathy is given, and when there is a partial or complete absence of cartilage a condition denominated Arthrosis occurs. Different from Chondromalacia, a cartilage affection, it is defined as a softening or a fissure of this surface. The most important aspect of it all is that Chondromlacia is an intra-operatory finding.

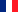
Figure. 21 clearly shows a normal left knee rich in cartilage and, osteoarthritis on the right. See the difference and contact between the bones.
This disease affects mostly women around the age of forty, is very rare before the age of thirty and is the most common osteoarthritis, followed by the hip.
he chondropathies and osteoarthritis can occur for many reasons:
- - The age factor is more related to the onset of osteoarthritis.
- - Obesity.
- - The generalized osteoarthritis.
- - The practice of impact sports such as football, soccer, basketball etc. for years can sometimes overload the joint leading it to osteoarthritis. It can also occur in construction workers.

Figure. 22. Obesity is a major cause of damage of the knee.
The secondary cause is a direct result of:
- Fetal development disorders (ie, occurring in uterus and during pregnancy) and knee dysplasia, which reduce the consistency, or degree of joint locks.
- - Fractures with fragments that are not in good postioning
- - Rheumatic Diseases.
- - Diseases caused by substance deposits in the joint.
- - Infections of the joints.
- - Not enough blood flow to the condyles in adults, which tend to collapse: the vascular osteonecrosis or bone necrosis.
- - Not enough blood flow to the growth cartilage of the knee (children and adolescents) that alter the way they articulate: it is osteochondritis (which can become completely detached and cause pain also known as pseudo latch locks.)
The image below shows an example.

Figure. 23. Dissecans Osteochondritis, with a detached fragment causing blockage.
- Removal of the meniscus, especially the lateral meniscus.
- Injuries to the ligaments that result in instability of the knee.
- Lateral collateral ligament injury that causes instability. The interior rarely suffers osteoarthritis.
- Excessive alterations in the axis of the knee: genu varus at attention when the knees are far apart ("cowboy leg"). Knock-knees, when the knees are close together but far apart ankles ("knock-knees"). Have to be very serious to cause osteoarthritis (Figure. 5 and Figure 6).
Treatment
For osteoarthritis or cartilage disorder treatment varies, taking into account the age, weight, what the person expects from the knee (a very active person will have different needs than less active or sedentary person).
What you must understand is the first time is; There are pain medications (act only against the pain similar to other pain relievers but they have recommended anti-inflammatory effects in acute crisis).

Figure. 24. Analgesics (pain killers) and anti-inflammatory
Rehabilitation
It is very important and is based on fitness training. In some cases may be associated cycles of relieving massages, electrotherapy and ultrasonic therapy in a specialized center for rehabilitation.

Figure. 25. Reeducation to strengthen your muscles.
The exercises that the patient does should tone the thigh muscles and stretch the joint. It should be progressive, smooth and painless to avoid ruptures, as the joint becomes stiff, and to avoid sudden friction on the cartilage already worn out.
You can also try administrating products within the knee (as shown in Figure 25) with the intention of relieving the symptoms of osteoarthritis (this procedure can be performed with a rheumatologist doctor or your surgeon).

Figure. 26. Infiltration of products to relieve pain temporarily.
And if all that fails, surgical treatment is the best option.
There are several ways we can speak of a total replacement of the cartilage, a partial replacement or a frequently used technique in France, Germany, Switzerland and USA are the osteotomies (Figure 29 shows a patient with osteoarthritis that is objective 5 degrees but is too young for joint replacement) temporary treatment lasting approximately 10 years

Figure. 27. Partial replacement of the cartilage of your knee.

Figure. 28. Total replacement of the cartilage of your knee.

Figure. 29. Osteotomy.
After joint replacement
You will be able towalk the same day of surgery, should remain in the institution 3 days, driving your car is usually possible within a month, a return visit is scheduled two months after the intervention with rehabilitation radiographs according to protocol.
The person suffering from osteoarthritis of the knee can follow the following guidelines for better quality of life and as an adjunct to medical treatment:
It is very important and is based on fitness training. In some cases may be associated cycles Relieving massage, electrotherapy and ultrasonic therapy in a specialized center for rehabilitation.
The exercises that the patient performs should tone the thigh muscles and stretch the joint. It Should be progressive, smooth and painless to avoid rupture, as the joint becomes stiff, and to avoid sudden friction on the cartilage already worn out.
Sometimes the damage is due to a Chondropathy, in these cases a minimum of cartilage replacement is possible using the same cartilage or a human tissue bank. These choices made in our center are known under the names of mosaic plasty, or a slightly larger graft known in Cartipache. Rarely have we been in need of replacing an entire condyle, but this procedure has been performed., Figures clearly show the two procedures.

Figure. 30. Mosaic plasty, on your left is an area where you take cartilage placed in surgical areas called zones of use.

Figure. 31. Cartipache; It shows a cartilage injury, a small amount of periostium is withdrawn, then cartilage grows and is then placed as a cure where cartilage was missing.