The knee
The knee joint is very important as it receives the entire burden of the body that comes from the spine and hip from our day to day, mainly from work, walk, and exercise.
The knee joint is made up of 3 chambers, between the femur, tibia and patella, each chamber is composed of cartilage, fibrous cartilage and ligaments, all of them in total harmony for the knee to function without pain. Pain can appear when walking, bearing weight, running, while sitting for long expanses of time, going up or down stairs, and stooping.

Figure. 1: normal anatomy of your knee
- Details
- Category: The knee
A sprain or strain is an injury of the ligaments stretching or twisting, accompanied by hematoma and inflammation and pain that prevents to continue moving the injured knee. Originated to be affected by mechanical action (the requirement of a sudden movement, or unnatural movement), or violence (fall, hit). Do not confuse with the dislocation, which is a more severe injury that involves changing the position of the joint and the separation of their bones. Or with the tear, which is injury to muscle tissue.
- Details
- Category: The knee
Inflammation of the Bags or membranes.
Within traumatic pathology, knee joint is probably the most studied, the pioneer in the field of arthroscopy, as mentioned before, it is a very important joint since it is in constant burden there are no bones that limit it; all boundaries are of soft tissue.
It is wholly surrounded by a joint capsule, forming a closed space. The inner cover of the capsule is the synovial membrane, whose primary mission is the secretion of fluid by the same name, which is fundamental to joint physiology with the purpose of lubrication and defense.
- Details
- Category: The knee
A discoid meniscus is a meniscus shaped disk or dish instead of having the characteristic of a meniscus semilunar form "C"; i.e. There is no central opening that allows you to increase the depth and improve the coupling. Some patients have discoid meniscus and have no symptoms, there are children begin their symptoms at an early age. The cause is unknown.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The surface of your knee is covered with an adhered, elastic tissue which fulfills an important role regarding joint harmony, this tissue is denominated cartilage, which lubricates, cushions blows, and gives stability to the knee. A small portion is may be injured in which case a condition known as chondropathy is given, and when there is a partial or complete absence of cartilage a condition denominated Arthrosis occurs. Different from Chondromalacia, a cartilage affection, it is defined as a softening or a fissure of this surface. The most important aspect of it all is that Chondromlacia is an intra-operatory finding.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The knee joint is subject to injury often in high-level athletes but also intermediate and low level ones as well. Lesions also can occur in elderly patients due to degenerative processes and violent contractions at a sharp bend of the knee, endangering the knee extensor apparatus by disruption of its elements at either the quadriceps tendon at its insertion into the pole top of the patella or the patellar tendon at its patellar insertion, or insertion into the anterior tibial tuberosity or body of the tendon.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The knee has 4 ligaments needed for its proper functioning, in short we can say that the knee joint can move forward, backward, flexed or extended and that all that is possible without pain and imbalance by ligaments. According to the type of physical activity (either walking or a sport) recalls each time one or more of the 4 ligaments.
- Details
- Category: The knee
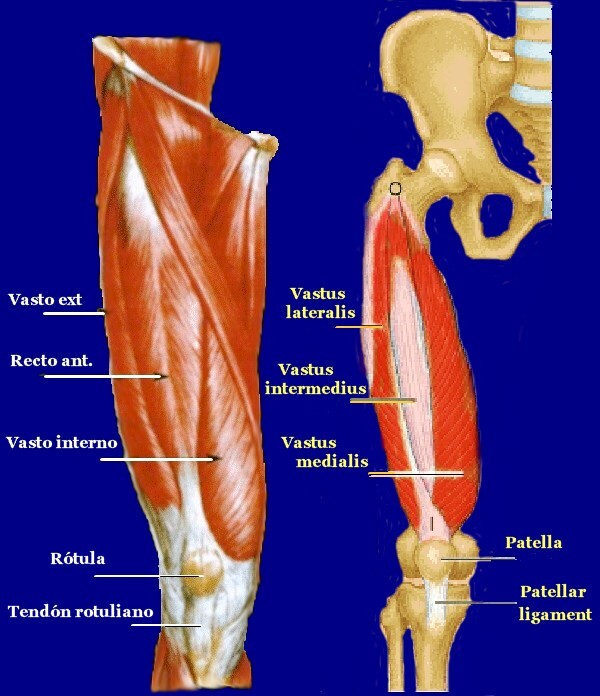
The front thigh muscles tension can be caused by problems such as poor posture, stiffness in the joints of the hip, the rigid spine or too much neural stimulation in the thigh and hip flexors. The rigidity of the hip can do that you can move the joints of the same in all ranges of motion, rotation, flexion and extension.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The meniscus act as shock absorbers of our weight, there are two, they create the proper functioning of the knee, allowing the bones not to collide between each other, but other than that it its an element which gives stability to the knee as well as lubrication, so in some injuries of ligaments, the meniscus is damaged, causing pain and instability. As shown in the picture above, we have two menisci toward one side inside and the outside.
- Details
- Category: The knee
Patellar instability refers to a condition through which the kneecap (patella) which plays an unusual mission, as a pulley on which rest the quadriceps and patellar tendons, cannot stay in the middle of the knee moving out (Figure. 34), resulting in pain, sometimes it does not move towards the outside but you feel it will, it is known as apprehension, this type of instability is due to a set of variations in anatomy, for example by oblique muscle fibers not inserted in their places, or just developing something that is known as the trochlea Figure. 35 (front segment covered by cartilage in Lemus where the patella slides), it most common in younger women with valgus deformity.
Doctor

The knee
The knee joint is very important as it receives the entire burden of the body that comes from the spine and hip from our day to day, mainly from work, walk, and exercise.
The knee joint is made up of 3 chambers, between the femur, tibia and patella, each chamber is composed of cartilage, fibrous cartilage and ligaments, all of them in total harmony for the knee to function without pain. Pain can appear when walking, bearing weight, running, while sitting for long expanses of time, going up or down stairs, and stooping.

Figure. 1: normal anatomy of your knee
- Details
- Category: The knee
A sprain or strain is an injury of the ligaments stretching or twisting, accompanied by hematoma and inflammation and pain that prevents to continue moving the injured knee. Originated to be affected by mechanical action (the requirement of a sudden movement, or unnatural movement), or violence (fall, hit). Do not confuse with the dislocation, which is a more severe injury that involves changing the position of the joint and the separation of their bones. Or with the tear, which is injury to muscle tissue.
- Details
- Category: The knee
Inflammation of the Bags or membranes.
Within traumatic pathology, knee joint is probably the most studied, the pioneer in the field of arthroscopy, as mentioned before, it is a very important joint since it is in constant burden there are no bones that limit it; all boundaries are of soft tissue.
It is wholly surrounded by a joint capsule, forming a closed space. The inner cover of the capsule is the synovial membrane, whose primary mission is the secretion of fluid by the same name, which is fundamental to joint physiology with the purpose of lubrication and defense.
- Details
- Category: The knee
A discoid meniscus is a meniscus shaped disk or dish instead of having the characteristic of a meniscus semilunar form "C"; i.e. There is no central opening that allows you to increase the depth and improve the coupling. Some patients have discoid meniscus and have no symptoms, there are children begin their symptoms at an early age. The cause is unknown.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The surface of your knee is covered with an adhered, elastic tissue which fulfills an important role regarding joint harmony, this tissue is denominated cartilage, which lubricates, cushions blows, and gives stability to the knee. A small portion is may be injured in which case a condition known as chondropathy is given, and when there is a partial or complete absence of cartilage a condition denominated Arthrosis occurs. Different from Chondromalacia, a cartilage affection, it is defined as a softening or a fissure of this surface. The most important aspect of it all is that Chondromlacia is an intra-operatory finding.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The knee joint is subject to injury often in high-level athletes but also intermediate and low level ones as well. Lesions also can occur in elderly patients due to degenerative processes and violent contractions at a sharp bend of the knee, endangering the knee extensor apparatus by disruption of its elements at either the quadriceps tendon at its insertion into the pole top of the patella or the patellar tendon at its patellar insertion, or insertion into the anterior tibial tuberosity or body of the tendon.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The knee has 4 ligaments needed for its proper functioning, in short we can say that the knee joint can move forward, backward, flexed or extended and that all that is possible without pain and imbalance by ligaments. According to the type of physical activity (either walking or a sport) recalls each time one or more of the 4 ligaments.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The front thigh muscles tension can be caused by problems such as poor posture, stiffness in the joints of the hip, the rigid spine or too much neural stimulation in the thigh and hip flexors. The rigidity of the hip can do that you can move the joints of the same in all ranges of motion, rotation, flexion and extension.
- Details
- Category: The knee
The meniscus act as shock absorbers of our weight, there are two, they create the proper functioning of the knee, allowing the bones not to collide between each other, but other than that it its an element which gives stability to the knee as well as lubrication, so in some injuries of ligaments, the meniscus is damaged, causing pain and instability. As shown in the picture above, we have two menisci toward one side inside and the outside.
- Details
- Category: The knee
Patellar instability refers to a condition through which the kneecap (patella) which plays an unusual mission, as a pulley on which rest the quadriceps and patellar tendons, cannot stay in the middle of the knee moving out (Figure. 34), resulting in pain, sometimes it does not move towards the outside but you feel it will, it is known as apprehension, this type of instability is due to a set of variations in anatomy, for example by oblique muscle fibers not inserted in their places, or just developing something that is known as the trochlea Figure. 35 (front segment covered by cartilage in Lemus where the patella slides), it most common in younger women with valgus deformity.
Information
- Interview - Radio 2016-08-05
- Normal knee Anatomy 2014-11-11
- Ankylosis, or Stiffness of the knee 2014-10-30
- Arthroscopy of the hip 2014-10-30
- Biomechanics of the knee 2014-11-11
- Hip dysplasia 2014-10-30
- Interview - Televen - 15/05/2015 2014-11-11
- Interviews 2014-11-10
- Knee sprain 2014-11-04
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip 2014-10-30
- The Arthrosis 2014-10-30
- The Patella 2014-10-30
- The Membranes 2014-10-30
- Injuries of the Knee Extensor Apparatus 2014-10-30
- The Ligament 2014-10-30
- The Meniscus 2014-10-30
- Dislocation of the patella 2014-11-11
- Discoid Meniscus 2014-11-04
- Total Knee prosthesis 2014-11-11
- Post prosthetic rehabilitation 2014-11-11
- Patella 2014-11-11
- Urgencia de Cadera 2014-10-31
- Urgencia de Columna Vertebral 2014-10-31
- Urgencia de Rodilla 2014-10-31